What exactly is autonomous Driving?
The term “independent driving” refers to an invention that permits vehicles to operate without the need for human interaction. There are a variety of levels of autonomy in driving, each having their own set of requirements and skills.
Autonomous Driving: Levels
The Society of Automotive Engineers has created six levels of independent driving (named Levels 0–5) and three levels of help highlights as well as three levels of automated driving elements.
1. Independent Driving Levels.
The three SAE levels that you start with of driving are levels of support which work when you drive regardless of whether or not using the pedals or steering. To ensure you are in control of your vehicle, you must be steering the boat and be focused on the road.
These highlights are limited to the following:
Flitting and alerts aid, for instance warnings to vulnerable sides or the slowing of a crisis programmed into
Guidance OR brake speed to increase backing, for instance, focus on the path or
Support for brake/speed increases and direction
Level 1 Driver Assistance
The higher level of independence driving is referred to as Level 1. At this stage the vehicle can operate independently under certain conditions However, the driver must always be expected to remain in control.
Certain typical examples in Level I independent driving are that it includes travel control (ACC) and Lane Keeping Assist (LKA). ACC lets the vehicle stay clear of the vehicle ahead of it is able to do so, while LKA ensures that the vehicle stays in its lane.
Both of these components rely on sensors to detect things around the vehicle. If there obstructions or vehicles within the path, ACC will dial back or stop the vehicle and LKA can alter the controls to maintain the vehicle on the direction it is in.
Independent Driving Levels 2 and 3.
The final three levels are where mechanized drive capabilities are used even when you’re not the driver however you’re at the wheel. These options don’t have being implemented, but your vehicle is likely to in all situation operate in a secure and controlled manner.
The conditions under which the vehicle can function are limited to a certain extent at these points, and the vehicle can only operate within specific limitations. The highest level of effectiveness is to have an independent vehicle in any circumstances.
The general availability of these levels of autonomy in driving is in the distant future, but numerous automakers have made efforts to extend the range of the Level 0 as well as Level 1 frameworks, while moving towards more computerized driving.
Level 2 2. Conditional Automation
This level allows drivers to be able to separate themselves from driving, but it is possible to assume the role under certain circumstances. Level 3 allows a car can monitor its surroundings as it moves to a different track, direct its movements the vehicle, slow down and increase speed over a slow-moving vehicle.
While you’re not able to sit on the couch for a rest in mid-afternoon but you are able to read, or text, and enjoy a cup of espresso when the car is in autonomous mode.
Stage 3: Complete Autonomous Driving
The highest degree of autonomy is referred to as the Level 5. This refers to a vehicle that is able to operate completely autonomously regardless of the circumstances and requires the absence of human information.
It also implies that the car can carry out a several activities simultaneously such as exploring, moving to a different track, and staying clear of the deterrents.
A few organizations in the automotive industry are testing Level 5 autonomous vehicles, but there is no self-driving vehicle that is yet available to the all of society.
ADAS Development against Autonomous Driving
Although ADAS data collection advancement and autonomous driving remain distinct, however they’re not the identical. ADAS are a feature which can be located in a variety of cutting-edge automobiles, while autonomous driving is a method that allows a vehicle to function without the assistance of humans. It is essentially, ADAS is on a level of autonomy that allows complete computerization of driving at the level of three.
The role of ADAS in autonomous Driving
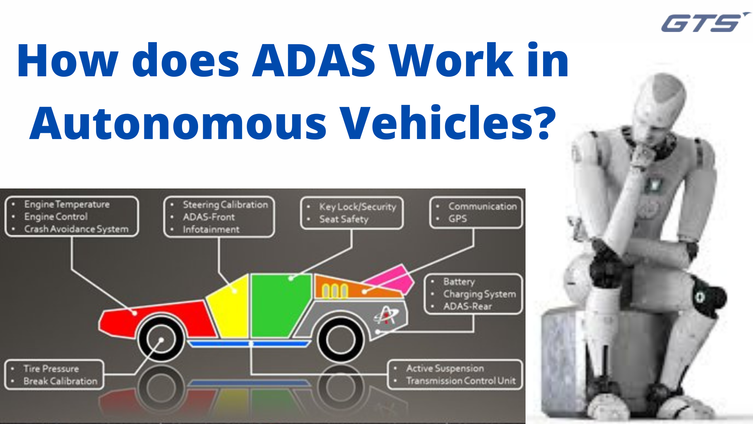
Although ADAS aren’t independent driver-specific frameworks for driving, they do play an important role in the planning of vehicles to be fully independent. Many of the elements that comprise the level I and Level II frameworks are made possible through ADAS. For example, ACC and LKA wouldn’t be feasible without sensors to detect objects in the vicinity of the vehicle. Furthermore the ADAS comprise LDW framework would not be as effective without cameras or other sensors that are able to monitor the vehicle’s movements in the open.
ADAS data collection is also essential for helping drivers learn to use autonomous driving systems. In learning how to use a vehicle equipped with ADAS features the drivers will be prepared to operate a vehicle fully autonomously. As the technology behind autonomous driving continues to advance it is likely that an increasing amount of vehicles will be fitted with ADAS features. Drivers must be aware of how to make use of the automated driving systems that are secure.
We hope that this article has answered your “ADAS or independent driving” concerns!
Learn more about: ADAS Have Changed the Auto Industry Forever. Here’s how:
While autonomous driving is in the future for many consumers, ADAS is here!
In addition, there is the need for adjustments following incidents like windshield replacement wheel arrangement, windshield replacement, and collisions.
In Car ADAS, we assist you in opening ADAS aligning focuses in order to make the world a safer place by adjusting the exact settings of ADAS in the event of mishaps. Contact us now!
What is the process for LiDAR function in self-driving car?
LIDAR is the abbreviation for Light Detection as well as Ranging. It is a technology for remote sensing emitting light which is reflected around an object before returning to the receiver where it creates points each time it touches the object. This creates a 3D model of the whole scene. We aid in the annotation or labeling of bicycles, pedestrians, cyclists, cars animals, trees and billboards, traffic lights garbage bins, etc. on this map by creating bounding boxes or cuboids specifically to train algorithmic machine learning to comprehend the world.
What is the process behind LiDAR Annotation work?
The LIDAR annotation identifies objects within the form of a 3D point cloud. It draw bounding cuboids around specific objects, returning the sizes and positions of the boxes.
LiDAR annotation is similar to image labeling but is different from the distinction in the real world because of a reason that is simple it is 3D-based of a flat screen. Additionally, humans need to work with a massive amount of points which aren’t confined by specific boundaries. Therefore, even for professional human beings, it’s difficult to determine the point that belongs to what object. If you zoom in on the point cloud image this problem becomes obvious.
An important role for LiDAR annotation
1.) Autonomous vehicles
LiDAR annotation and ADAS annotation technology helps ML algorithms by making the semantic and in-situ segmenting of lengthy sequences of LiDAR data extremely efficient and precise. It is now possible to separate those long sequences with a minimum of time, and with amazing results.
The most significant type of Data Annotation i.e. Lidar annotation integrated with machine Learning and Data Annotation, as well as Data Labeling has helped in various ways to provide precise and efficient results. LiDAR has seen major modifications in the last few years and the most significant thing is that it is becoming increasingly important due to its essential role in autonomous vehicles that allow us to be able to safely navigate our roads.
SEMANTIC Annotation

Semantic Segmentation is a well-known Computer Vision problem that involves using as input raw data (2D 3D images) and then labeling the regions of interest that need to be highlighted. In Semantic Segmentation we perform the process of clustering several components of images to the same class of object. Utilize our fully-managed, human-powered segmentation of images at pixel level and annotation to construct the most precise semantic segmentation tasks on a pixel size.
It is the latest technology we can use to provide the self-driven car a greater degree of precision. By using Semantic Segmentation we can classify all of the pixels in an image into relevant categories of objects. The classes we create can be “semantically capable of interpretation” and relate to the real-world categories. Learning Spiral offers you the best experience in this area of LiDAR to create algorithms for your autonomous vehicle.
Segmentation semantically is a method of separating 3D LiDAR data in dynamic scenes to enable self-driving applications. A system for semantic segmentation based on 3D LiDAR data, which includes the segmentation of images in range, sample generation tracking-level data associations, interframe-based data and semi-supervised learning is created. The quantitative and qualitative tests demonstrate that the combination of just a few annotations and a significant quantity of constraint data increases the effectiveness and flexibility, which results in more than 10 percent increase.
How GTS can help you?
Global Technology Solutions understands the need of having high-quality, precise datasets to train, test, and validate your models. As a result, we deliver 100% accurate and quality tested datasets. Image data collection, Speech datasets, Text datasets, and Video datasets are among the datasets we offer. We offer services in over 200 languages.
.png)
.png)

.png)
Comments
Post a Comment